Arduino - Actuador con retroalimentación
En un tutorial anterior, hemos aprendido sobre el actuador lineal sin retroalimentación. En este tutorial, vamos a aprender sobre el actuador lineal con retroalimentación (también conocido como el actuador lineal con retroalimentación). La retroalimentación del actuador lineal proporciona la información para identificar la posición de su recorrido y luego controlar la posición. En detalle, vamos a aprender:
- Cómo funciona un actuador lineal con retroalimentación
- Cómo encontrar la posición del actuador lineal con retroalimentación (en milímetros)
- Cómo controlar la posición de un actuador lineal
Hardware Requerido
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables STEM V3 Starter Kit (Arduino included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Acerca del actuador lineal con realimentación
Un actuador lineal con retroalimentación es un actuador lineal que tiene una señal de retroalimentación que permite identificar su posición y controlarlo. La retroalimentación es un potenciómetro que genera un voltaje proporcional a la posición del recorrido.
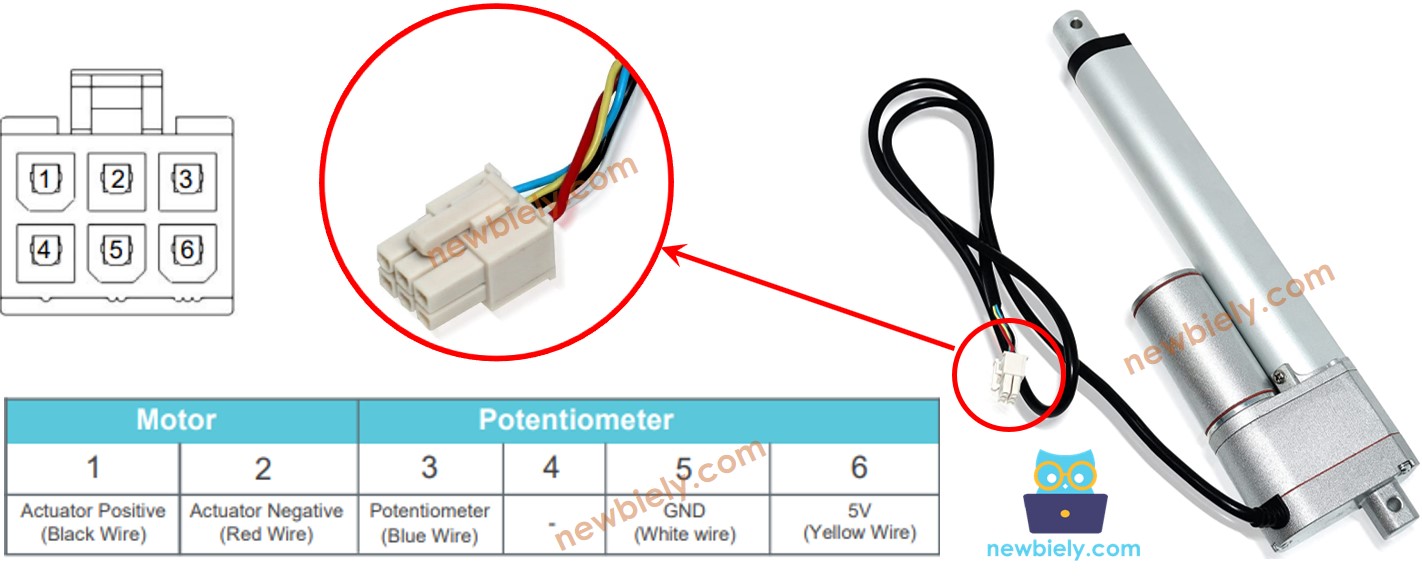
Pinout del actuador lineal de retroalimentación
Un actuador lineal de retroalimentación tiene 5 cables:
- Cable positivo del actuador: Este cable se utiliza para controlar el actuador lineal utilizando voltaje alto (12V, 24V, 48V...).
- Cable positivo del actuador: Este cable se utiliza para controlar el actuador lineal utilizando voltaje alto (12V, 24V, 48V...).
- Cable de 5V: Este cable se utiliza para el potenciómetro de retroalimentación. Conecte este cable a 5V o 3.3V.
- Cable de tierra: Este cable se utiliza para el potenciómetro de retroalimentación. Conecte este cable a tierra.
- Cable del potenciómetro: (también llamado cable de retroalimentación, o cable de salida) Este cable proporciona el valor de voltaje en proporción a la posición del recorrido.
Cómo funciona
Si proporcionamos alta tensión a los cables positivos y negativos, el recorrido del actuador se extenderá o retraerá. En detalle, si conectamos:
- 12 V (12 V, 24 V, 48 V, ...) y GND al cable positivo y al cable negativo, respectivamente: el actuador lineal se extiende a plena velocidad hasta que alcance el tope.
- 12 V (12 V, 24 V, 48 V, ...) y GND al cable negativo y al cable positivo, respectivamente: el actuador lineal se retrae a plena velocidad hasta que alcance el tope.
- Mientras se extiende o se retrae, si dejamos de alimentar al actuador (GND a ambos cables, positivo y negativo), el actuador deja de extenderse/retraerse.
※ Nota:
- El valor de voltaje para controlar el actuador depende de la especificación del actuador. Consulte la hoja de datos o el manual para conocer el valor de voltaje correspondiente.
- El actuador puede mantener la posición incluso cuando se detiene la alimentación mientras soporta una carga.
El valor de voltaje en el potenciómetro es proporcional a la posición de la carrera del actuador. Al medir este voltaje, podemos conocer la posición de la carrera.
Diagrama de cableado
Por favor, retire los tres jumpers del módulo L298N antes de cablear.
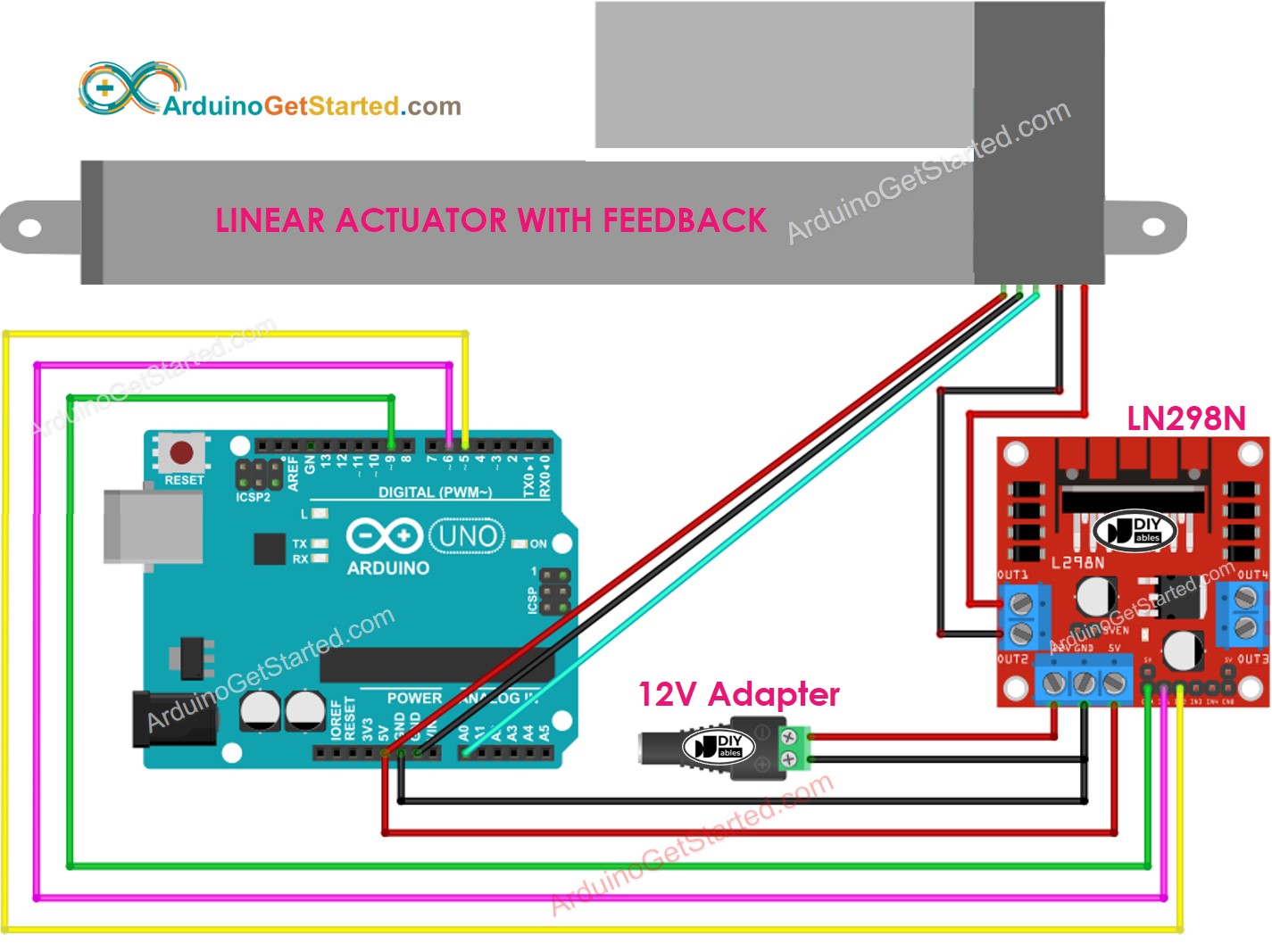
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Cómo controlar la extensión y la retracción de un actuador lineal
Ver Arduino - Actuador tutorial
Cómo encontrar la posición del actuador lineal
A continuación se muestra cómo identificar la posición del recorrido en un actuador lineal.
Calibración
- Identifica la longitud del recorrido del actuador (en milímetros) midiendo (con una regla) o leyendo la hoja de datos
- Identifica los valores de salida cuando el actuador lineal está completamente extendido y completamente retraído al ejecutar el código que se muestra a continuación
- Verás el registro en el Monitor Serial como en el siguiente ejemplo
- Anota estos valores
- Si los valores mínimos y máximos están invertidos, intercambia IN1_PIN e IN2_PIN
Código de Arduino que calcula la posición del actuador
- Actualizar los tres valores calibrados en el código
- Cargar el código en Arduino
- Ver el resultado en el Monitor serie
Cómo controlar un actuador lineal para alcanzar una posición específica
Video Tutorial
Estamos considerando crear tutoriales en video. Si considera que los tutoriales en video son importantes, suscríbase a nuestro canal de YouTube para motivarnos a crear los videos.
