ESP32 - Botón - Zumbador piezoeléctrico
Este tutorial le explica cómo usar el ESP32, un botón y un zumbador piezoeléctrico para hacer lo siguiente:
- ESP32 emite un sonido cuando se pulsa un botón y se detiene cuando ese botón NO está pulsado.
- ESP32 reproduce una melodía si se pulsa un botón.
Hardware Requerido
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables ESP32 Starter Kit (ESP32 included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Acerca del zumbador piezoeléctrico y del botón
Tenemos tutoriales específicos sobre el zumbador piezoeléctrico y el botón. Cada tutorial contiene información detallada e instrucciones paso a paso sobre la distribución de pines de hardware, el principio de funcionamiento, la conexión de cableado al ESP32 y el código para ESP32... Obtén más información sobre ellos en los siguientes enlaces:
Por favor, tenga en cuenta que este tutorial utiliza un zumbador de 3-5 V, pero puede adaptarlo para un zumbador de 12 V. Puede aprender sobre Tutorial de Zumbador ESP32
Diagrama de Cableado
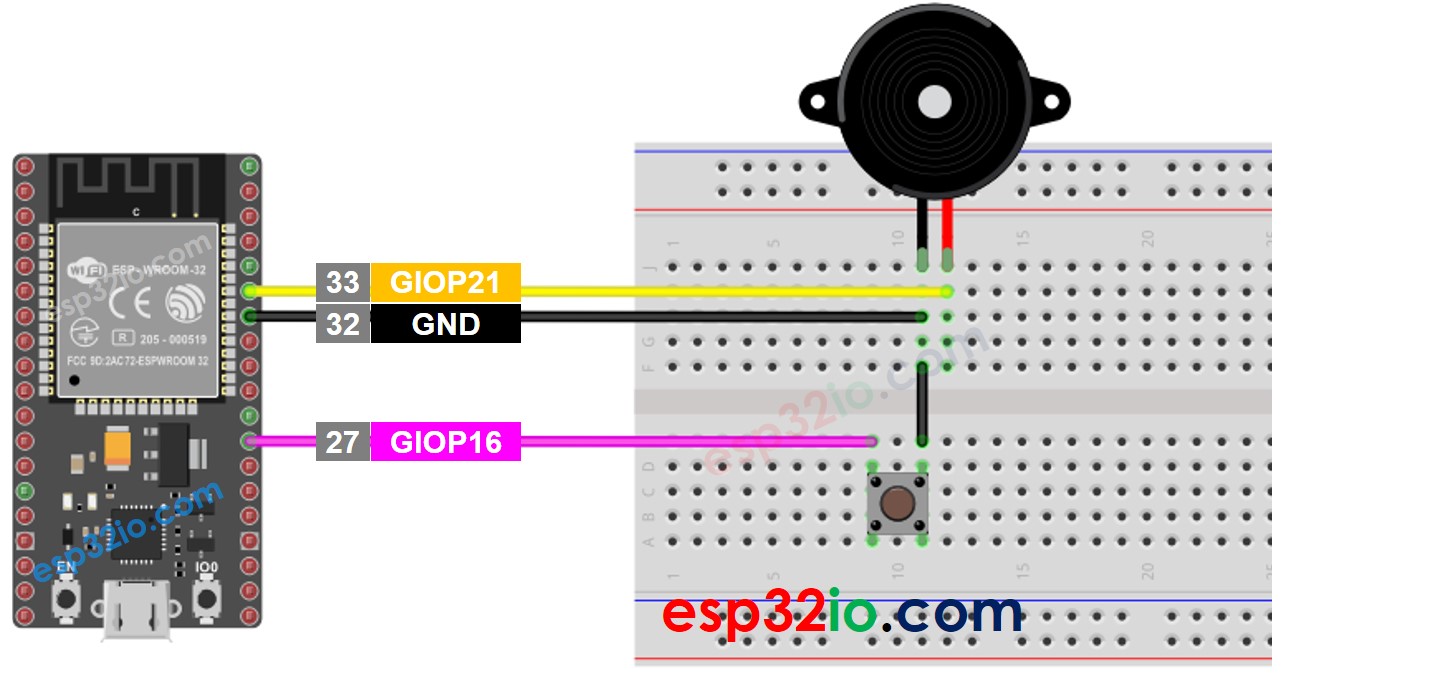
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Si no sabe c\u00f3mo alimentar ESP32 y otros componentes, encuentre instrucciones en el siguiente tutorial: C\u00f3mo alimentar ESP32.
Código ESP32 - Sonido Simple
Pasos R\u00e1pidos
- Si es la primera vez que usas ESP32, consulta cómo configurar el entorno para ESP32 en Arduino IDE.
- Realiza el cableado tal como se muestra en la imagen de arriba.
- Conecta la placa ESP32 a tu PC mediante un cable USB micro.
- Abre Arduino IDE en tu PC.
- Selecciona la placa ESP32 adecuada (p. ej. ESP32 Dev Module) y el puerto COM.
- Copia el código anterior y pégalo en Arduino IDE.
- Compila y sube el código a la placa ESP32 haciendo clic en el botón Upload en Arduino IDE.
- Presiona y mantén presionado el botón durante varios segundos.
- Escucha el sonido del zumbador piezoeléctrico.
Explicación línea por línea del código
El código ESP32 anterior contiene una explicación línea por línea. ¡Por favor lea los comentarios del código!
ESP32 Código - Melodía
Pasos R\u00e1pidos
- Copie el código anterior y péguelo en Arduino IDE.
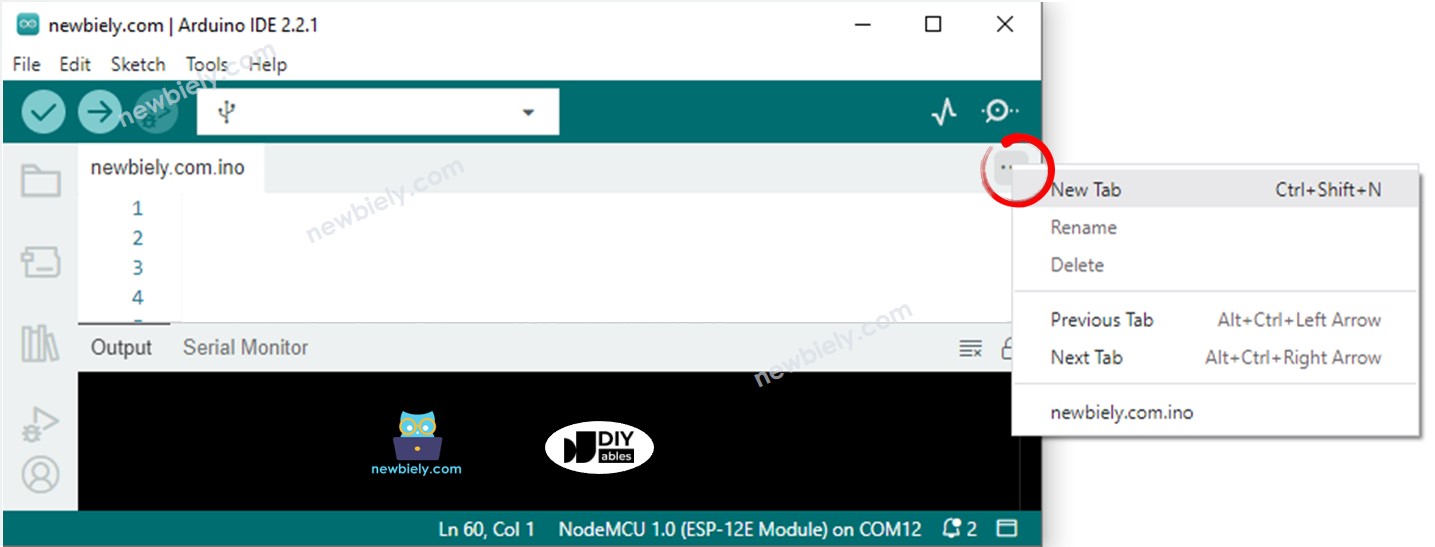
- Cree el archivo pitches.h en Arduino IDE haciendo:
- Haga clic en el botón justo debajo del icono del monitor serie y elija Nueva pestaña, o use las teclas Ctrl+Shift+N.
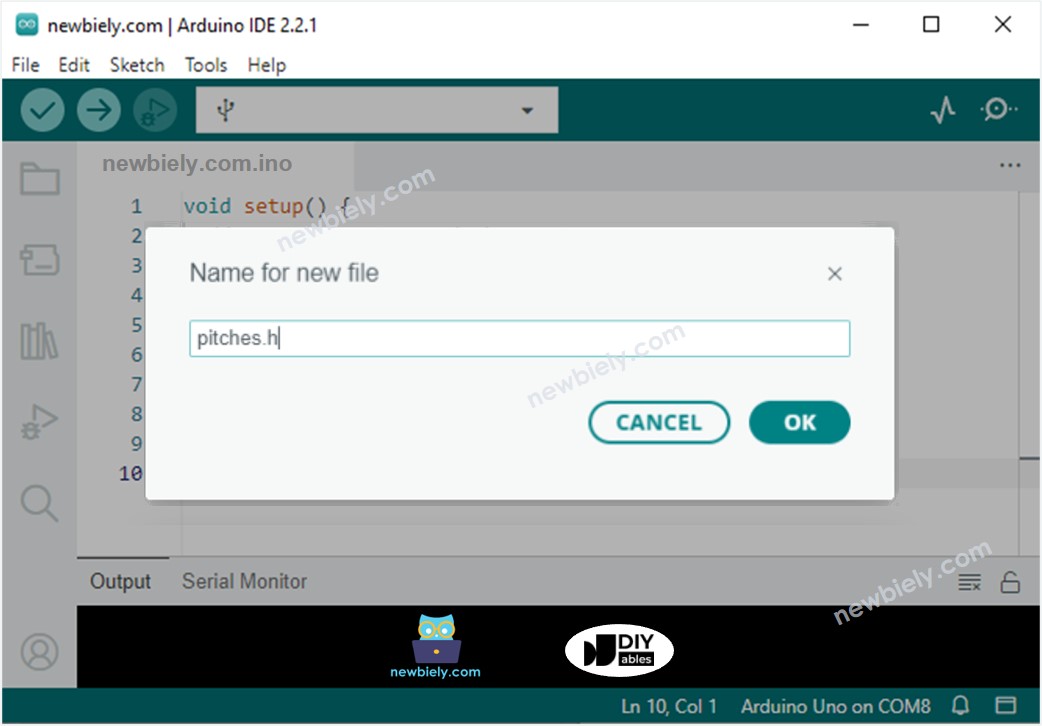
- Asigna el nombre del archivo pitches.h y haz clic en el botón OK
- Copie el código que se muestra a continuación y péguelo en el archivo pitches.h creado.
- Compilar y subir código a la placa ESP32 haciendo clic en el botón Subir en la IDE de Arduino
- Pulsa el botón
- Escucha la melodía del zumbador piezoeléctrico
Explicación del código línea por línea
El código ESP32 anterior contiene una explicación línea por línea. ¡Por favor lea los comentarios del código!
※ Nota:
El código anterior usa la función delay(). Esto bloquea el resto del código durante la reproducción de la melodía. Para evitar bloquear el resto del código, use la biblioteca ezBuzzer en su lugar. Esta biblioteca está diseñada para que el zumbador emita pitidos o reproduzca melodía sin bloquear el resto del código.
Video Tutorial
Estamos considerando crear tutoriales en video. Si considera que los tutoriales en video son importantes, suscríbase a nuestro canal de YouTube para motivarnos a crear los videos.
