ESP8266 - LED - Parpadeo sin retardo
Imaginemos que ESP8266 tiene dos tareas por realizar: parpadear un LED y monitorear el estado de un botón que puede ser presionado en cualquier momento. Si usamos la función delay() (como se explicó en un tutorial anterior), ESP8266 podría perder algunas pulsaciones del botón. En otras palabras, ESP8266 no podría ejecutar completamente la segunda tarea.
Este tutorial le enseña cómo hacer que el ESP8266 parpadee un LED y monitorizar el estado de un botón sin perder ninguna de sus pulsaciones.
Vamos a repasar tres ejemplos y a comparar las diferencias entre ellos:
- ESP8266 parpadea un LED con la función delay()
- ESP8266 parpadea un LED con la función millis()
- ESP8266 parpadea un LED con la librería ezLED
Este método no se limita solo a parpadear un LED y a comprobar el estado del botón. En general, permite que el ESP8266 realice varias tareas de forma simultánea sin bloquearse entre ellas.
Hardware Requerido
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Buy Note: Use the LED Module for easier wiring. It includes an integrated resistor.
Acerca de LED y Botón
Si no está familiarizado con el LED y con el botón (disposición de pines, funcionalidad, programación ...), los siguientes tutoriales pueden ayudar:
Diagrama de Cableado
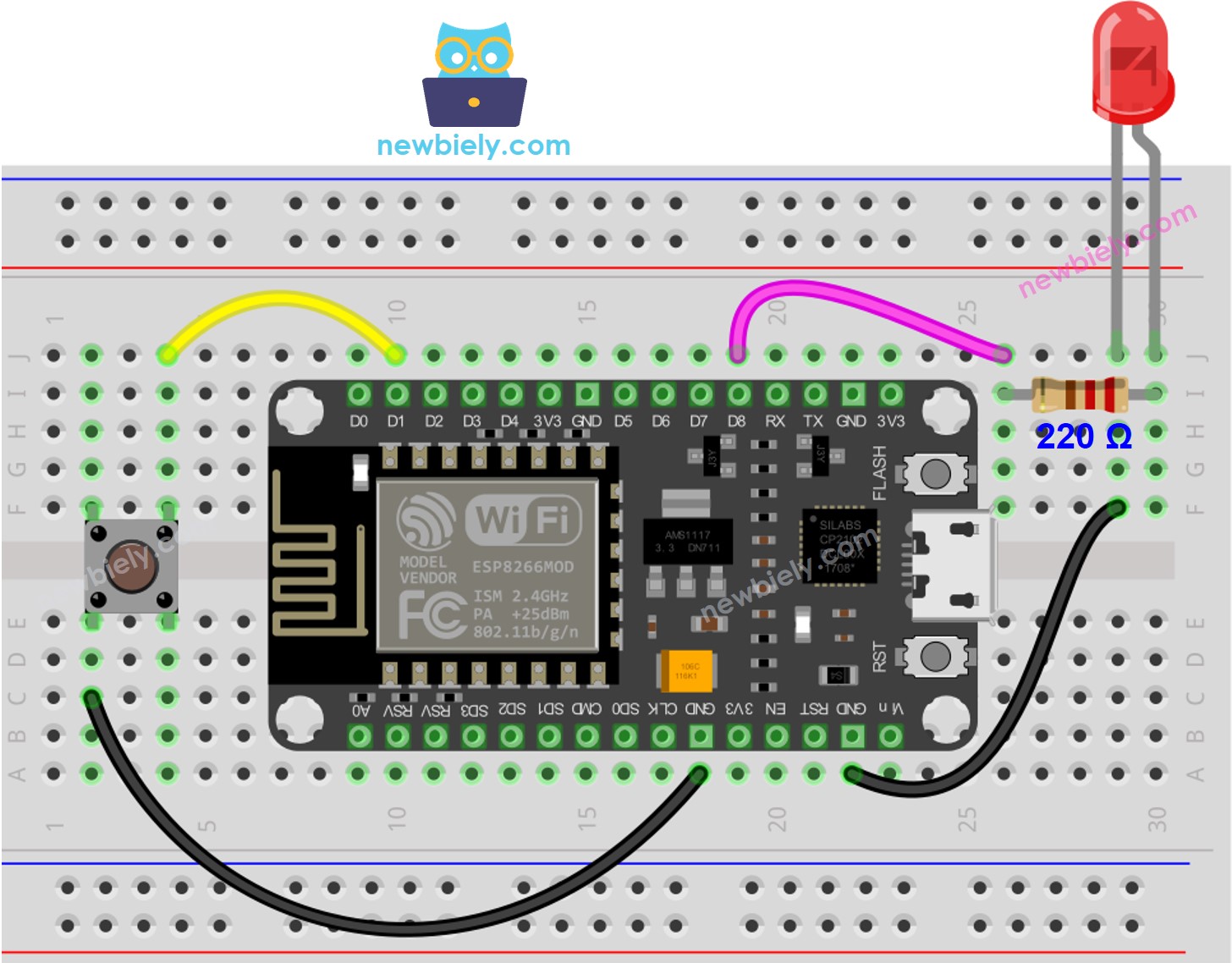
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Para obtener m\u00e1s informaci\u00f3n, consulte Pines del ESP8266 y c\u00f3mo alimentar ESP8266 y otros componentes.
Código ESP8266 - Con Retardo
Pasos R\u00e1pidos
Para empezar con ESP8266 en el IDE de Arduino, siga estos pasos:
- Consulta el tutorial cómo configurar el entorno para ESP8266 en Arduino IDE si es la primera vez que usas ESP8266.
- Conecta los componentes tal como se muestran en el diagrama.
- Conecta la placa ESP8266 a tu ordenador mediante un cable USB.
- Abre Arduino IDE en tu ordenador.
- Elige la placa ESP8266 correcta, como (p. ej. NodeMCU 1.0 (Módulo ESP-12E)), y su puerto COM respectivo.
- Conecta el cable USB a la ESP8266 y al ordenador.
- Inicia Arduino IDE, selecciona la placa y el puerto correctos.
- Copia el código y ábrelo en Arduino IDE.
- Haz clic en el botón Subir en Arduino IDE para compilar y subir el código al ESP8266.
- Abre el Monitor Serial.
- Pulsa el botón cuatro veces.
- Observa el LED; se encenderá y apagará cada segundo.
- Verifica la salida en el Monitor Serial.
- En el Monitor Serial, algunas pulsaciones no se registraron. Esto se debe a que, durante la demora, el ESP8266 no puede realizar ninguna tarea. En consecuencia, no puede detectar el evento de pulsación.
Código ESP8266 - Sin demora
Pasos R\u00e1pidos
- Conecta los componentes tal como se muestra en el diagrama.
- Conecta la placa ESP8266 a tu computadora usando un cable USB.
- Abre el Arduino IDE en tu computadora.
- Elige la placa ESP8266 correcta, como (p. ej. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), y su puerto COM correspondiente.
- Ejecuta el código y pulsa el botón 4 veces.
- Observa el LED, que alternará entre ENCENDIDO y APAGADO a intervalos regulares de un segundo.
- Revisa la salida en el Monitor Serial.
- Se identificaron todas las ocurrencias de asuntos urgentes.
Explicación del código
¡Consulta la explicación línea por línea que se encuentra en los comentarios del código fuente!
Añadiendo más tareas
El código ESP8266 que se muestra a continuación hace
- Hace que dos LEDs parpadeen con intervalos diferentes.
- Verifica el estado del botón.
Video Tutorial
Estamos considerando crear tutoriales en video. Si considera que los tutoriales en video son importantes, suscríbase a nuestro canal de YouTube para motivarnos a crear los videos.
Extensibilidad
Este método permite al ESP8266 realizar varias tareas al mismo tiempo, sin que una tarea bloquee a otra. Por ejemplo, enviar una solicitud a Internet y esperar la respuesta, mientras también se parpadean los indicadores LED y se supervisa el botón de cancelación.
