ESP8266 - Ethernet
Esta guía te muestra cómo conectar el ESP8266 a Internet o a tu red local utilizando el módulo Ethernet W5500. A continuación, estos son los temas que trataremos:
- Conectar ESP8266 con el módulo Ethernet W5500
- Programar ESP8266 para solicitudes web a través de Ethernet
- Crear un servidor web básico en ESP8266 con Ethernet
Hardware Requerido
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
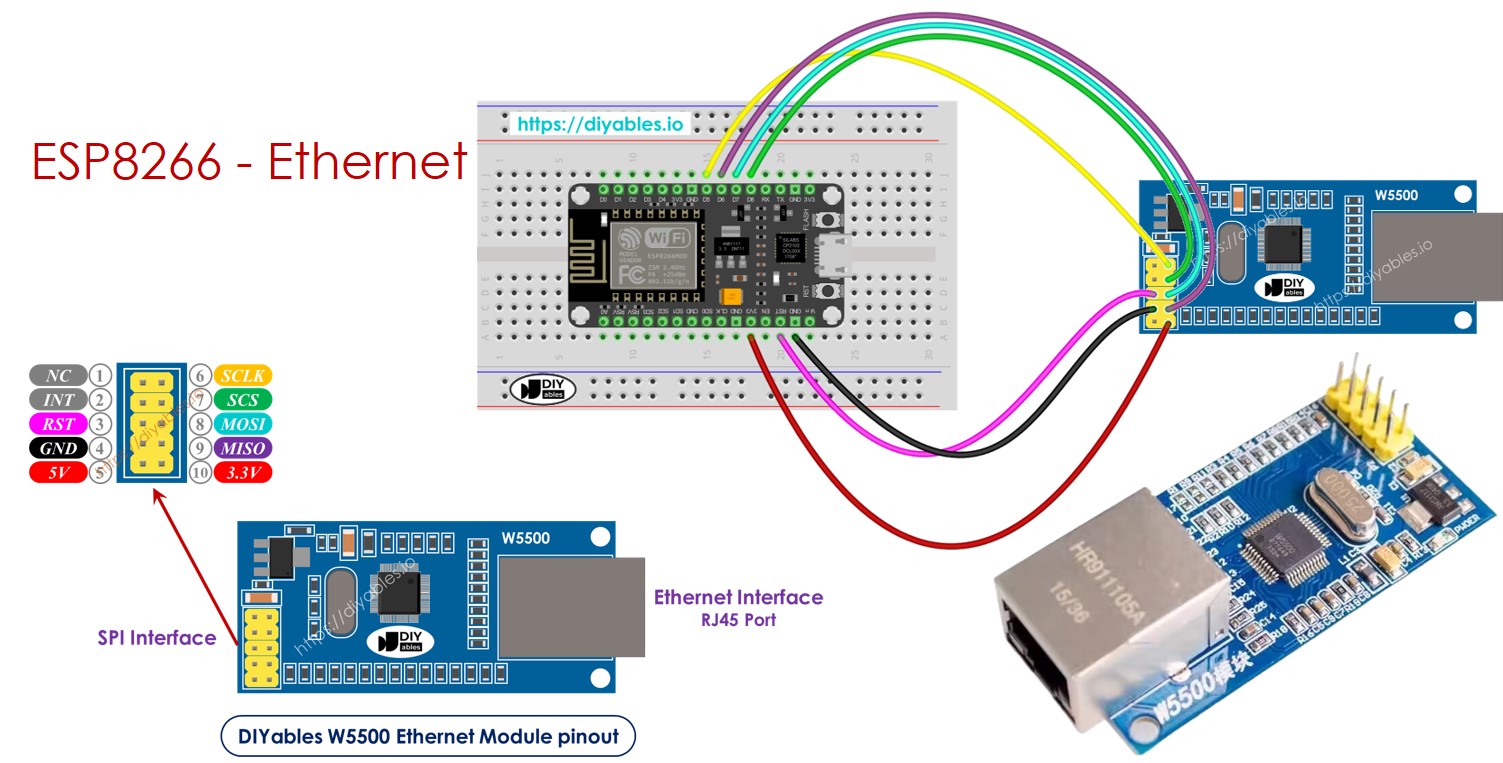
Acerca del módulo Ethernet W5500
El módulo Ethernet W5500 tiene dos tipos de conexiones:
- Interfaz RJ45: Conéctelo a un dispositivo de red como un enrutador o un conmutador usando un cable Ethernet.
- Interfaz SPI: Conéctelo a una placa ESP8266 usando las siguientes conexiones para sus 10 pines:
- Pin NC: Deje este pin sin conectar.
- Pin INT: Deje este pin sin conectar.
- Pin RST: Conéctelo al pin de reinicio (EN) en el ESP8266.
- Pin GND: Conéctelo al pin de tierra (GND) en el ESP8266.
- Pin 5V: No conecte este pin.
- Pin 3.3V: Conéctelo al pin de 3.3V en el ESP8266.
- Pin MISO: Conéctelo al pin SPI MISO en el ESP8266.
- Pin MOSI: Conéctelo al pin SPI MOSI en el ESP8266.
- Pin SCS: Conéctelo al pin SPI CS (Chip Select) en el ESP8266.
- Pin SCLK: Conéctelo al pin SPI SCK (Reloj) en el Arauthenticated.
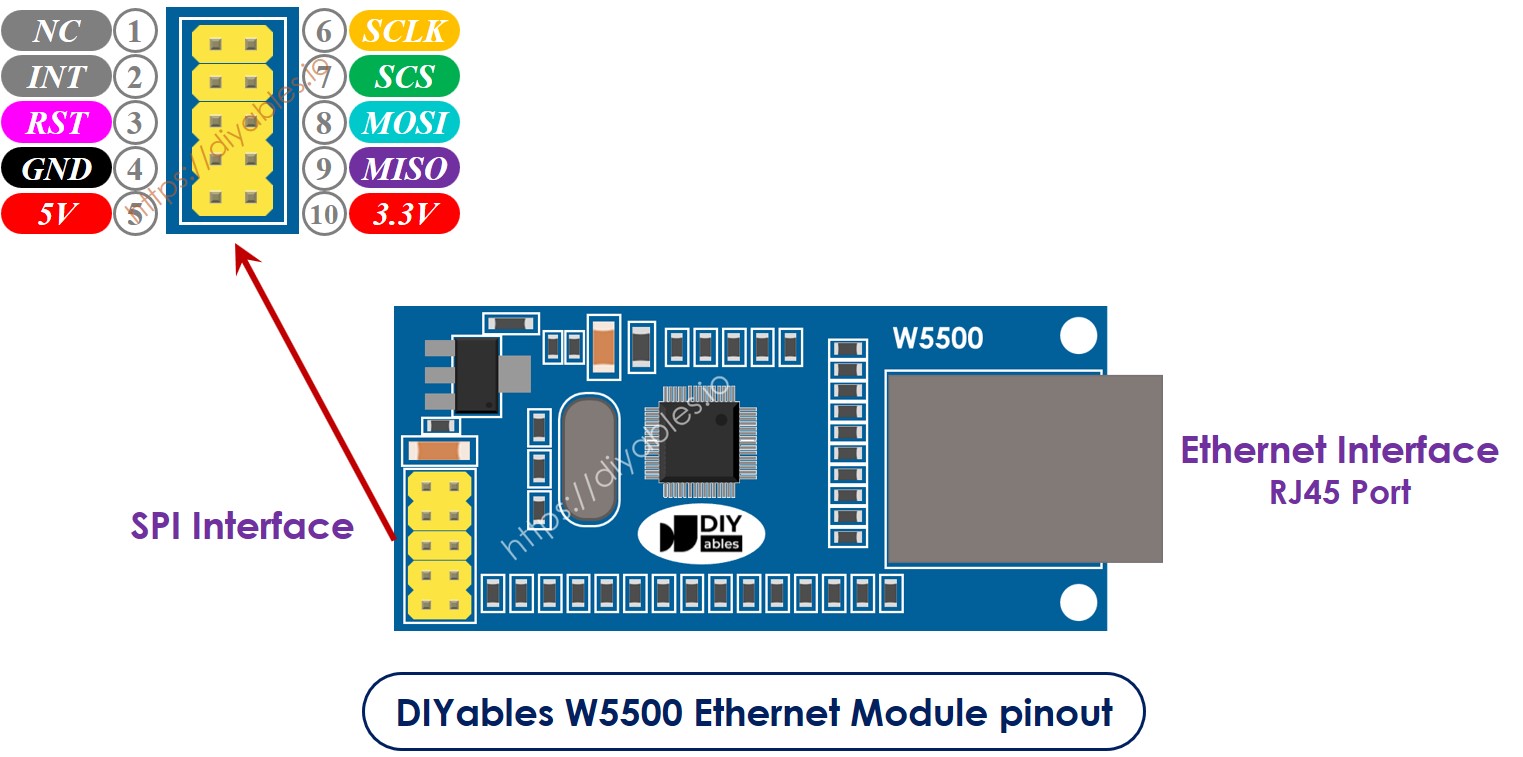
Diagrama de cableado entre ESP8266 y el módulo Ethernet W5500
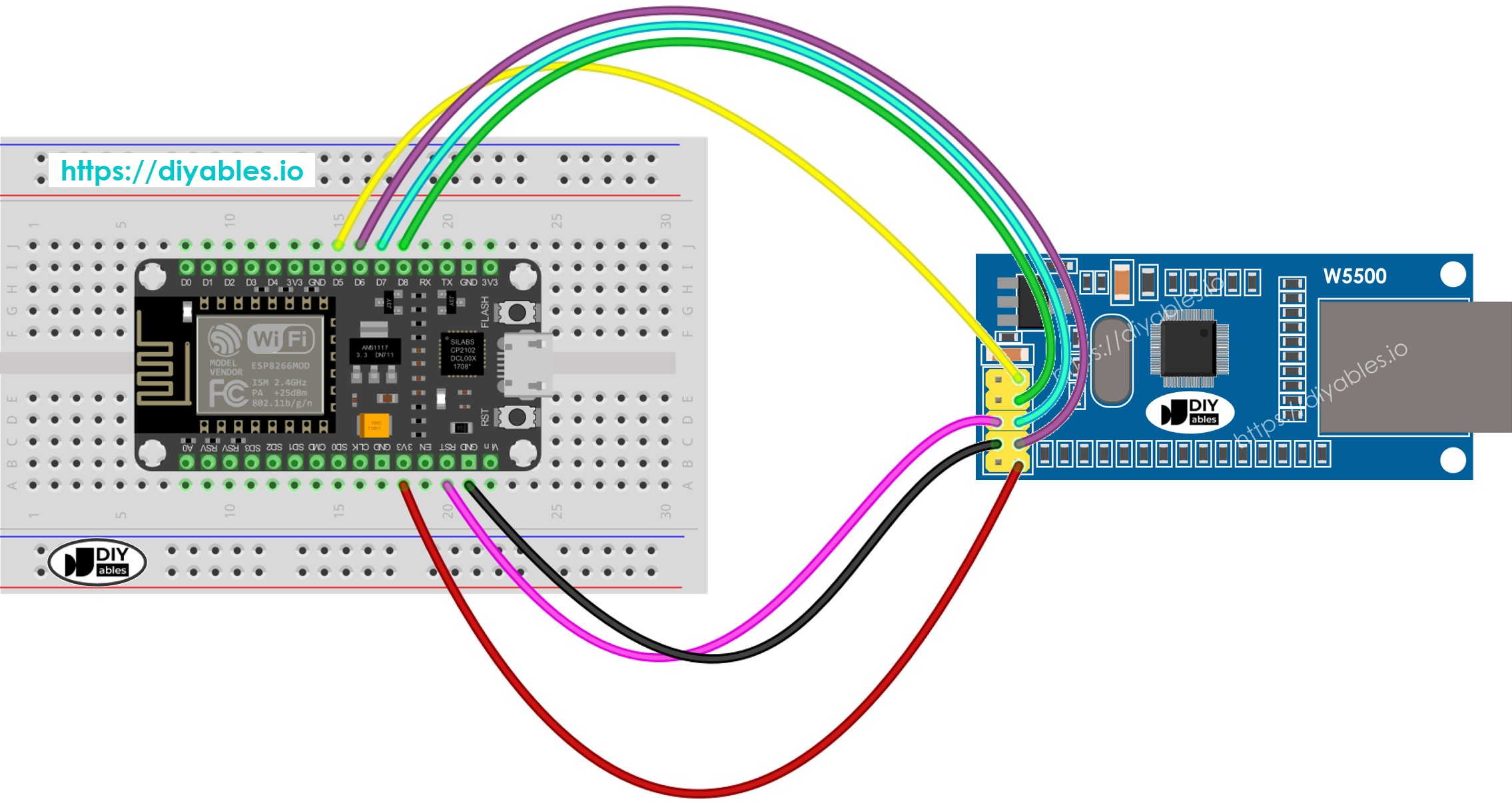
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
Para obtener m\u00e1s informaci\u00f3n, consulte Pines del ESP8266 y c\u00f3mo alimentar ESP8266 y otros componentes.
Código ESP8266 para el Módulo Ethernet - Realizar una solicitud HTTP a través de Ethernet
Este código funciona como un cliente web. Envía solicitudes HTTP al servidor web en http://example.com/.
Pasos R\u00e1pidos
Para empezar con ESP8266 en el IDE de Arduino, siga estos pasos:
- Consulta el tutorial cómo configurar el entorno para ESP8266 en Arduino IDE si es la primera vez que usas ESP8266.
- Conecta el módulo Ethernet a la placa ESP8266 como se muestra en el diagrama de cableado.
- Usa un cable Ethernet para conectar el módulo Ethernet a tu router o switch.
- Conecta la placa ESP8266 a tu ordenador usando un cable USB.
- Abre Arduino IDE en tu ordenador.
- Elige la placa ESP8266 correcta, por ejemplo (p. ej. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), y su puerto COM correspondiente.
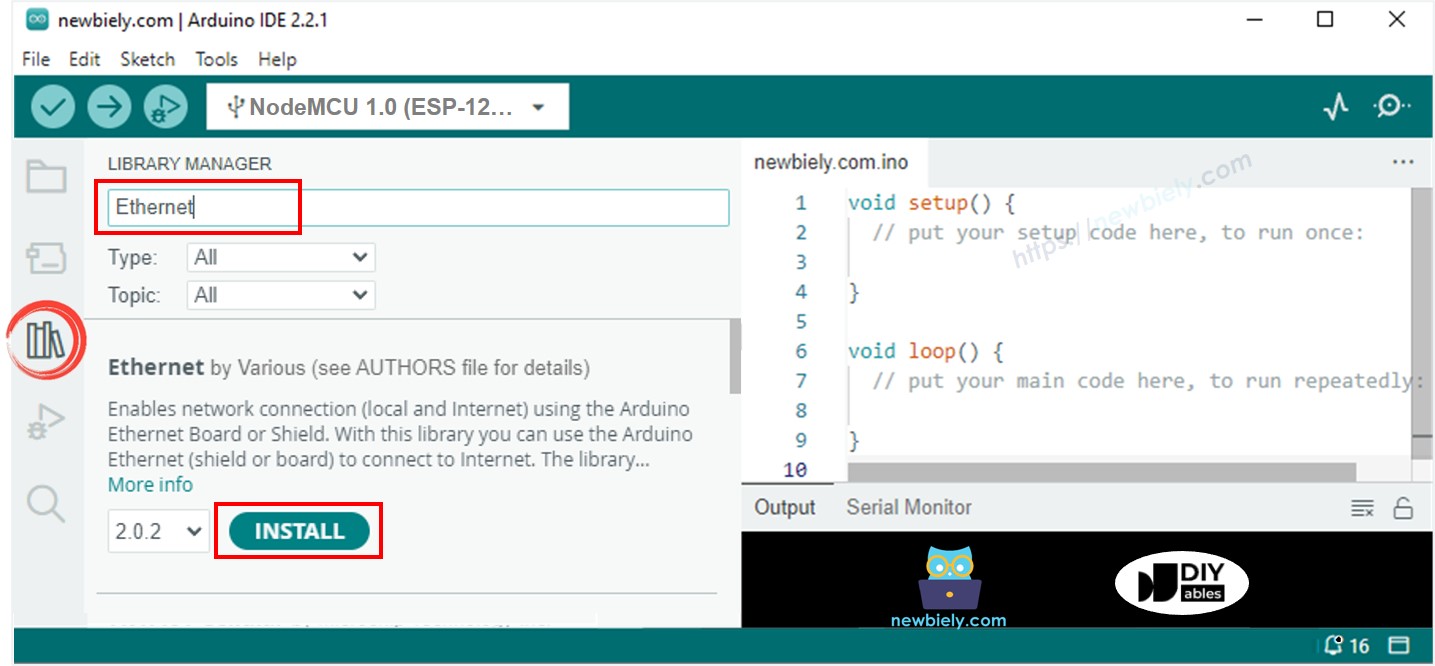
- Haz clic en el icono Bibliotecas en la barra izquierda del Arduino IDE.
- Busca Ethernet, luego encuentra la biblioteca Ethernet de Various.
- Haz clic en el botón Instalar para instalar la biblioteca Ethernet.
- Abre el Monitor Serial en el IDE de Arduino.
- Copia el código proporcionado y pégalo en el IDE de Arduino.
- Presiona el botón Subir en el IDE de Arduino para enviar el código al ESP25.
- Consulta el resultado en el Monitor Serial, el cual mostrará el resultado como se muestra a continuación.
※ Nota:
Si otro dispositivo en la misma red tiene la misma dirección MAC, podría no funcionar correctamente.
Código ESP8266 para el módulo Ethernet - Servidor web
El código a continuación transforma el ESP8266 en un servidor web. Este servidor entrega una página web básica a los navegadores de Internet.
Pasos R\u00e1pidos
- Copia el código anterior y pégalo en el IDE de Arduino.
- Haz clic en el botón Subir en el IDE de Arduino para transferir el código al ESP8266.
- Verifica los resultados en el Monitor serie; se mostrarán tal como se describen.
- Copie la dirección IP dada arriba y introdúzcala en la barra de direcciones de su navegador. Verá una página web simple mostrada por el ESP8266.