ESP8266 - Módulo RTC DS1307
Este tutorial te enseña cómo usar el ESP8266 para leer la fecha y la hora desde el módulo RTC DS1307. En detalle, aprenderemos:
Cómo conectar el módulo DS1307 de reloj en tiempo real al ESP8266.
Cómo programar el ESP8266 para leer la fecha y la hora (segundo, minuto, hora, día de la semana, día del mes, mes y año) desde el módulo RTC DS1307.
Cómo programar el ESP8266 para crear horarios diarios utilizando el módulo RTC DS1307.
Cómo programar el ESP8266 para crear horarios semanales utilizando el módulo RTC DS1307.
Cómo programar el ESP8266 para crear horarios en una fecha específica utilizando el módulo RTC DS1307.
Or you can buy the following kits:
Divulgación: Algunos de los enlaces proporcionados en esta sección son enlaces de afiliado de Amazon. Podemos recibir una comisión por las compras realizadas a través de estos enlaces sin costo adicional para usted. Apreciamos su apoyo.
ESP8266 tiene ciertas funciones relacionadas con el tiempo, por ejemplo millis(), micros(). Sin embargo, estas no pueden proporcionar la fecha y la hora (segundos, minutos, horas, día, fecha, mes y año). Para obtener la fecha y la hora, se debe usar un módulo de Reloj en Tiempo Real (RTC) como DS3231 o DS1370. El módulo DS3231 tiene una mayor precisión que el DS1370. Para obtener más información, consulte DS3231 vs DS1307.
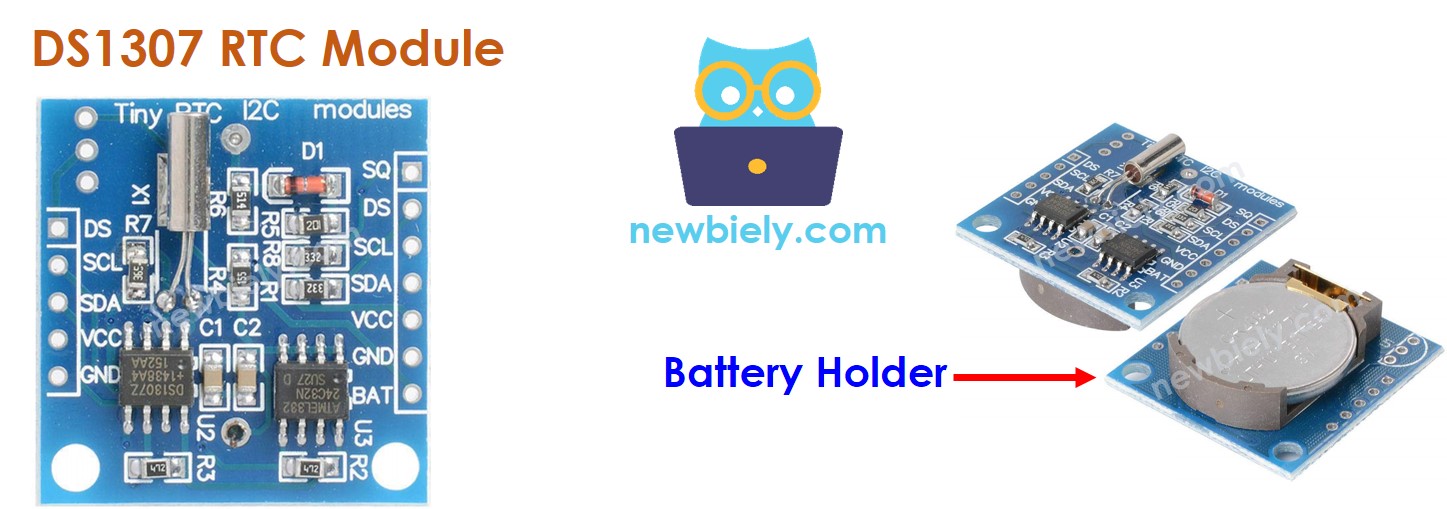
El módulo DS1307 de reloj en tiempo real tiene 12 pines, pero para uso normal requiere 4 pines: VCC, GND, SDA y SCL.
El pin SCL: es un pin de reloj serial para la interfaz I2C.
El pin SDA: es un pin de datos seriales para la interfaz I2C.
El pin VCC: suministra energía al módulo. Puede ir desde 3.3V hasta 5.5V.
El pin GND: es el pin de tierra.
El módulo DS1307 tiene un soporte para la batería que, al insertar una batería CR2032, mantiene la hora en el módulo cuando la alimentación principal está apagada. Sin la batería, la información de la hora se perderá si se desconecta la alimentación principal y será necesario restablecerla.
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
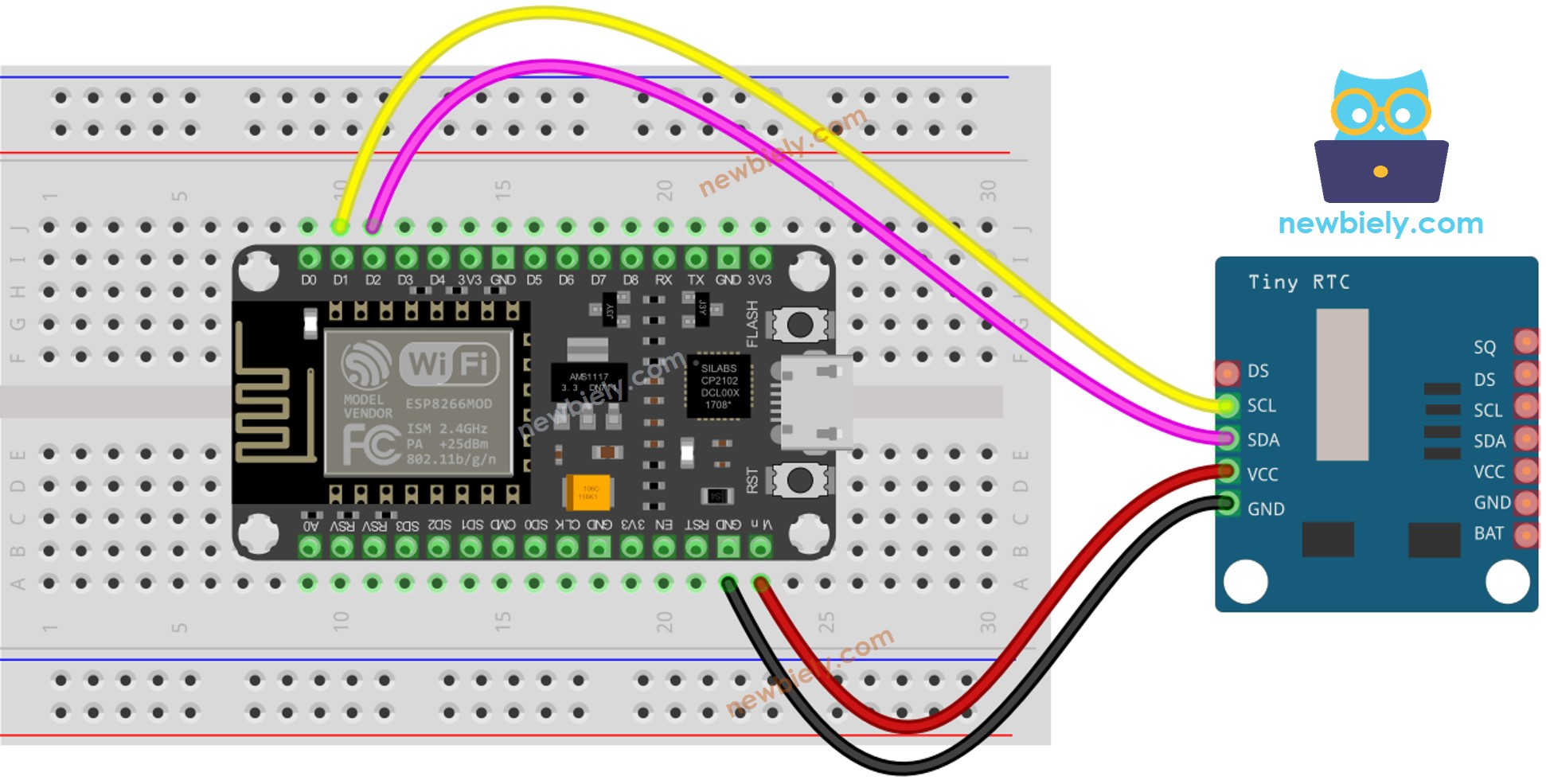
Para obtener m\u00e1s informaci\u00f3n, consulte Pines del ESP8266 y c\u00f3mo alimentar ESP8266 y otros componentes.
| DS1307 RTC Module | ESP8266 |
|---|
| Vin | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| SDA | GPIO4 |
| SCL | GPIO5 |
if (! rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
while (1);
}
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
DateTime now = rtc.now();
Serial.print("Date & Time: ");
Serial.print(now.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(now.dayOfTheWeek());
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(now.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(now.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.println(now.second(), DEC);
#include <RTClib.h>
RTC_DS1307 rtc;
char daysOfTheWeek[7][12] = {
"Sunday",
"Monday",
"Tuesday",
"Wednesday",
"Thursday",
"Friday",
"Saturday"
};
void setup () {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (! rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
Serial.flush();
while (1);
}
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
}
void loop () {
DateTime now = rtc.now();
Serial.print("Date & Time: ");
Serial.print(now.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(daysOfTheWeek[now.dayOfTheWeek()]);
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(now.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(now.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.println(now.second(), DEC);
delay(1000);
}
Para empezar con ESP8266 en el IDE de Arduino, sigue estos pasos:
Conecta los componentes como se muestra en el diagrama.
Conecta la placa ESP8266 a tu computadora usando un cable USB.
Abre el Arduino IDE en tu computadora.
Selecciona la placa ESP8266 correcta, como (p. ej. NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)), y su puerto COM correspondiente.
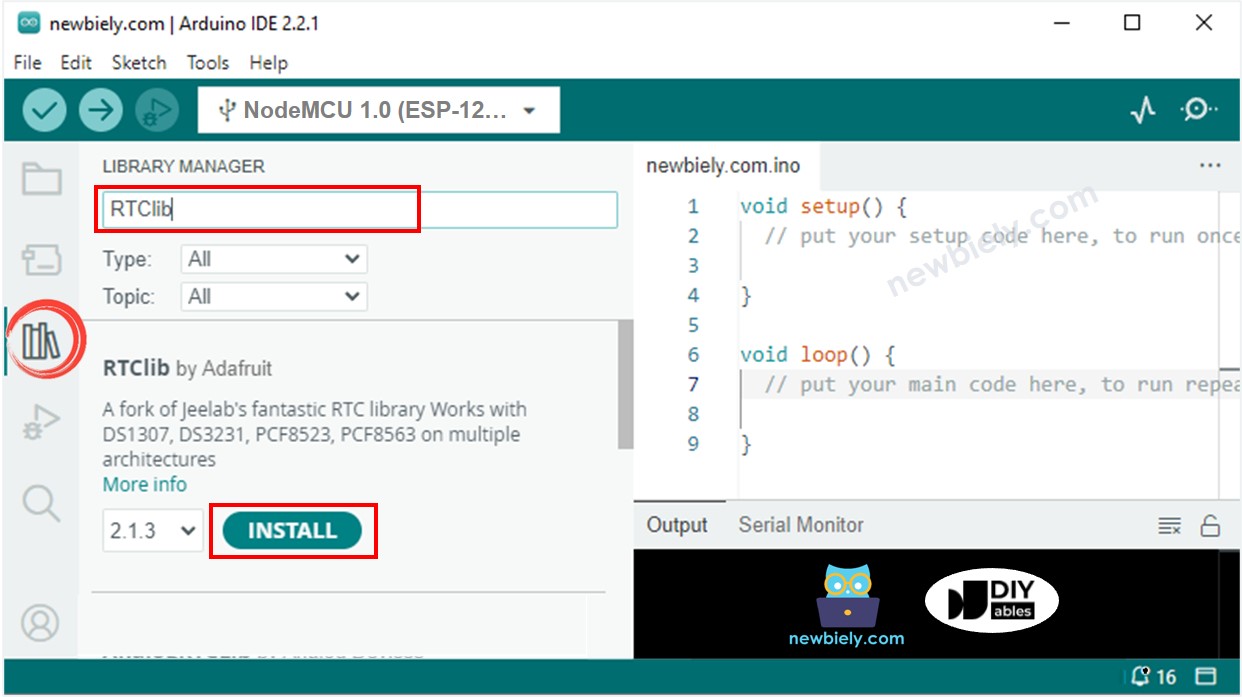
Haz clic en el icono Bibliotecas en la barra izquierda del Arduino IDE.
Busca “RTClib” y localiza la biblioteca RTC de Adafruit.
Presiona el botón Instalar para agregar la biblioteca RTC.
Copia el código y ábrelo en el IDE de Arduino.
Haz clic en el botón Subir en el IDE de Arduino para compilar y subir el código al ESP8266.
Abre el Monitor serie.
Consulta el resultado en el Monitor serie.
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 9:9:35
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 9:9:36
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 9:9:37
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 9:9:38
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 9:9:39
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 9:9:40
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 9:9:41
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 9:9:42
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 9:9:43
Date & Time: 2021/10/6 (Wednesday) 9:9:44
#include <RTClib.h>
uint8_t DAILY_EVENT_START_HH = 13;
uint8_t DAILY_EVENT_START_MM = 50;
uint8_t DAILY_EVENT_END_HH = 14;
uint8_t DAILY_EVENT_END_MM = 10;
RTC_DS1307 rtc;
char daysOfTheWeek[7][12] = {
"Sunday",
"Monday",
"Tuesday",
"Wednesday",
"Thursday",
"Friday",
"Saturday"
};
void setup () {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (! rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
while (1);
}
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
}
void loop () {
DateTime now = rtc.now();
if (now.hour() >= DAILY_EVENT_START_HH &&
now.minute() >= DAILY_EVENT_START_MM &&
now.hour() < DAILY_EVENT_END_HH &&
now.minute() < DAILY_EVENT_END_MM) {
Serial.println("It is on scheduled time");
} else {
Serial.println("It is NOT on scheduled time");
}
printTime(now);
}
void printTime(DateTime time) {
Serial.print("TIME: ");
Serial.print(time.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(time.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(time.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(daysOfTheWeek[time.dayOfTheWeek()]);
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(time.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(time.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.println(time.second(), DEC);
}
#include <RTClib.h>
#define SUNDAY 0
#define MONDAY 1
#define TUESDAY 2
#define WEDNESDAY 3
#define THURSDAY 4
#define FRIDAY 5
#define SATURDAY 6
uint8_t WEEKLY_EVENT_DAY = MONDAY;
uint8_t WEEKLY_EVENT_START_HH = 13;
uint8_t WEEKLY_EVENT_START_MM = 50;
uint8_t WEEKLY_EVENT_END_HH = 14;
uint8_t WEEKLY_EVENT_END_MM = 10;
RTC_DS1307 rtc;
char daysOfTheWeek[7][12] = {
"Sunday",
"Monday",
"Tuesday",
"Wednesday",
"Thursday",
"Friday",
"Saturday"
};
void setup () {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (! rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
while (1);
}
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
}
void loop () {
DateTime now = rtc.now();
if (now.dayOfTheWeek() == WEEKLY_EVENT_DAY &&
now.hour() >= WEEKLY_EVENT_START_HH &&
now.minute() >= WEEKLY_EVENT_START_MM &&
now.hour() < WEEKLY_EVENT_END_HH &&
now.minute() < WEEKLY_EVENT_END_MM) {
Serial.println("It is on scheduled time");
} else {
Serial.println("It is NOT on scheduled time");
}
printTime(now);
}
void printTime(DateTime time) {
Serial.print("TIME: ");
Serial.print(time.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(time.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(time.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(daysOfTheWeek[time.dayOfTheWeek()]);
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(time.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(time.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.println(time.second(), DEC);
}
#include <RTClib.h>
#define SUNDAY 0
#define MONDAY 1
#define TUESDAY 2
#define WEDNESDAY 3
#define THURSDAY 4
#define FRIDAY 5
#define SATURDAY 6
#define JANUARY 1
#define FEBRUARY 2
#define MARCH 3
#define APRIL 4
#define MAY 5
#define JUNE 6
#define JULY 7
#define AUGUST 8
#define SEPTEMBER 9
#define OCTOBER 10
#define NOVEMBER 11
#define DECEMBER 12
DateTime EVENT_START(2021, AUGUST, 15, 13, 50);
DateTime EVENT_END(2021, SEPTEMBER, 29, 14, 10);
RTC_DS1307 rtc;
char daysOfTheWeek[7][12] = {
"Sunday",
"Monday",
"Tuesday",
"Wednesday",
"Thursday",
"Friday",
"Saturday"
};
void setup () {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (! rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
Serial.flush();
while (1);
}
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
}
void loop () {
DateTime now = rtc.now();
if (now.secondstime() >= EVENT_START.secondstime() &&
now.secondstime() < EVENT_END.secondstime()) {
Serial.println("It is on scheduled time");
} else {
Serial.println("It is NOT on scheduled time");
}
printTime(now);
}
void printTime(DateTime time) {
Serial.print("TIME: ");
Serial.print(time.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(time.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(time.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(daysOfTheWeek[time.dayOfTheWeek()]);
Serial.print(") ");
Serial.print(time.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(time.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.println(time.second(), DEC);
}
Estamos considerando crear tutoriales en video. Si considera que los tutoriales en video son importantes, suscríbase a nuestro canal de YouTube para motivarnos a crear los videos.
※ NUESTROS MENSAJES
No dude en compartir el enlace de este tutorial. Sin embargo, por favor no use nuestro contenido en otros sitios web. Hemos invertido mucho esfuerzo y tiempo en crear el contenido, ¡por favor respete nuestro trabajo!