Ejemplo de Arduino WebJoystick - Tutorial de Control de Joystick Virtual
Visión general
El ejemplo WebJoystick crea una interfaz de joystick virtual accesible desde cualquier navegador web. Diseñado para Arduino Uno R4 WiFi y DIYables STEM V4 IoT plataforma educativa con capacidades robóticas mejoradas, características de control de motor integradas y una integración perfecta con módulos educativos de robótica. Perfecto para controlar robots, vehículos o cualquier sistema que requiera entrada de posición en 2D.
Características
- Joystick Virtual: Control de joystick interactivo a través de la interfaz web
- Coordenadas en Tiempo Real: Valores X/Y de -100 a +100 para un control preciso
- Soporte Táctil y de Ratón: Funciona en computadoras de escritorio, tabletas y dispositivos móviles
- Retorno Automático Configurable: Opción para que el joystick vuelva al centro cuando se libere
- Control de Sensibilidad: Sensibilidad ajustable para evitar actualizaciones excesivas
- Retroalimentación Visual: Visualización de posición en tiempo real y valores de coordenadas
- Comunicación WebSocket: Respuesta instantánea sin actualizar la página
- Posición Central: Indicador claro de posición central para un control neutro
- Plataforma Extensible: Actualmente implementado para Arduino Uno R4 WiFi, pero puede ampliarse para otras plataformas de hardware. Ver DIYables_WebApps_ESP32
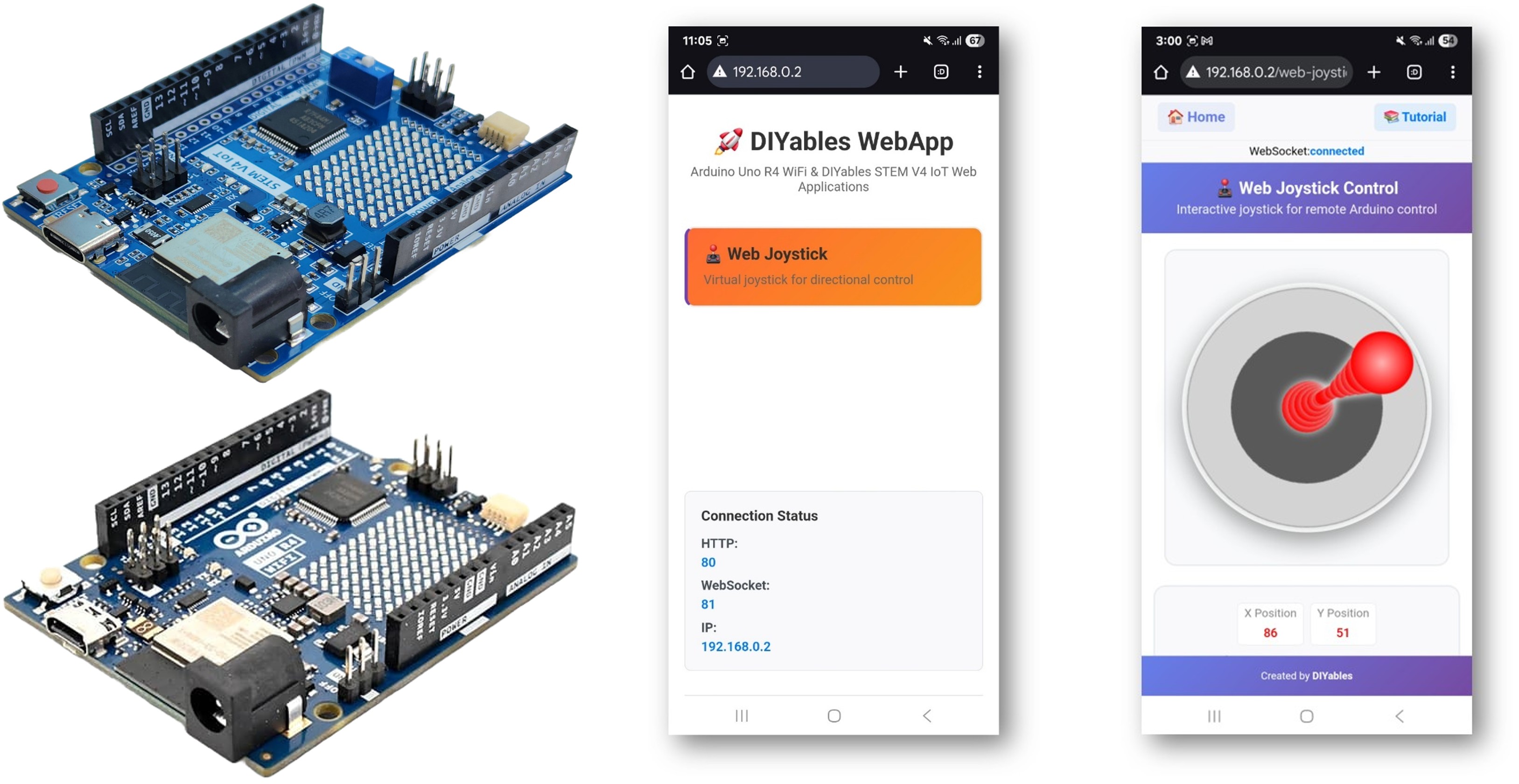
Hardware Requerido
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables STEM V4 IoT Starter Kit (Arduino included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Instrucciones de Configuración
Pasos rápidos
Siga estas instrucciones paso a paso:
- Si es la primera vez que usas el Arduino Uno R4 WiFi/DIYables STEM V4 IoT, consulta el tutorial sobre configurar el entorno para Arduino Uno R4 WiFi/DIYables STEM V4 IoT en el IDE de Arduino.
- Conecta la placa Arduino Uno R4/DIYables STEM V4 IoT a tu ordenador usando un cable USB.
- Abre el IDE de Arduino en tu ordenador.
- Selecciona la placa adecuada Arduino Uno R4 (por ejemplo, Arduino Uno R4 WiFi) y el puerto COM.
- Navega hasta el icono Bibliotecas en la barra izquierda del IDE de Arduino.
- Busca "DIYables WebApps", luego encuentra la biblioteca DIYables WebApps de DIYables.
- Haz clic en el botón Instalar para instalar la biblioteca.
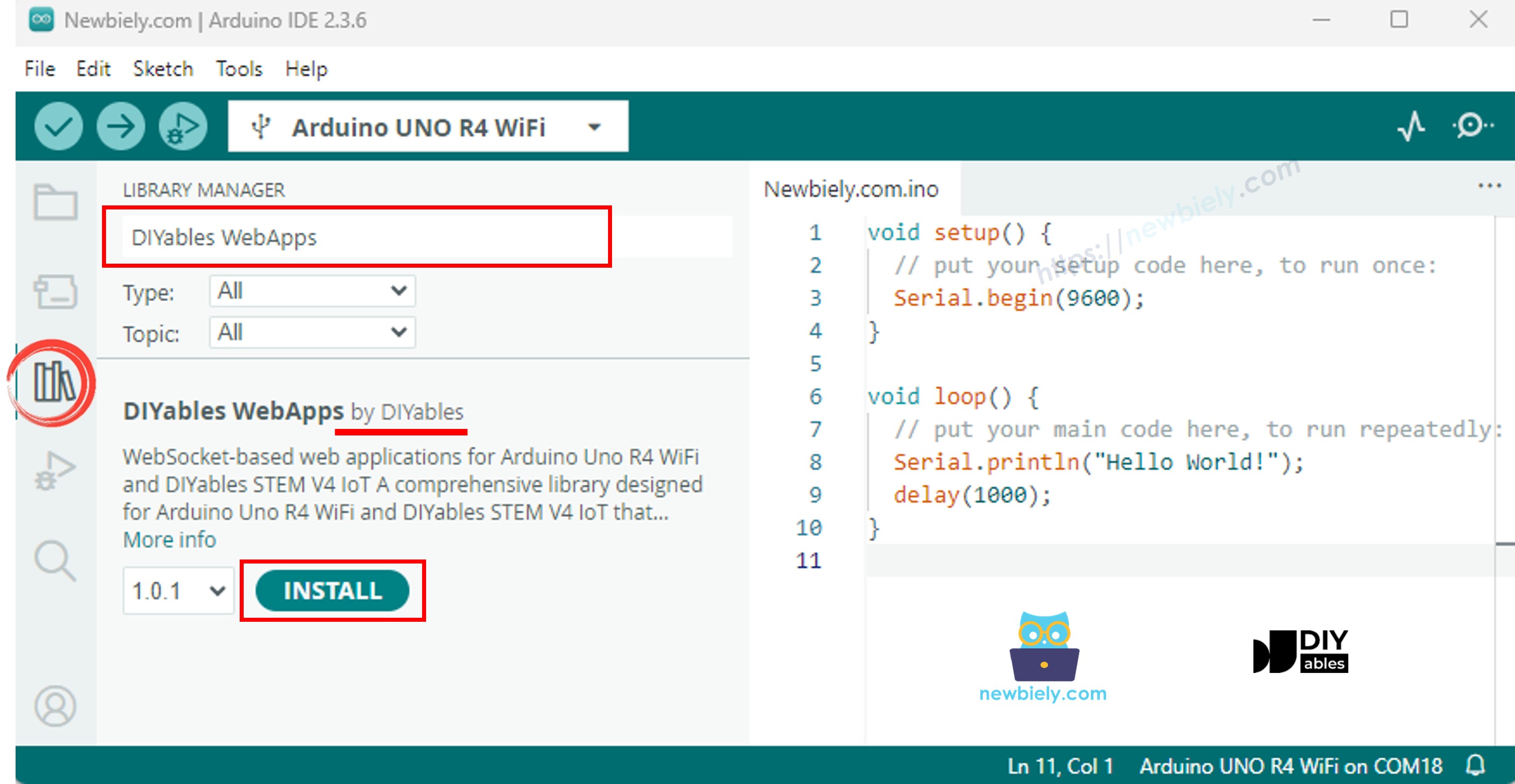
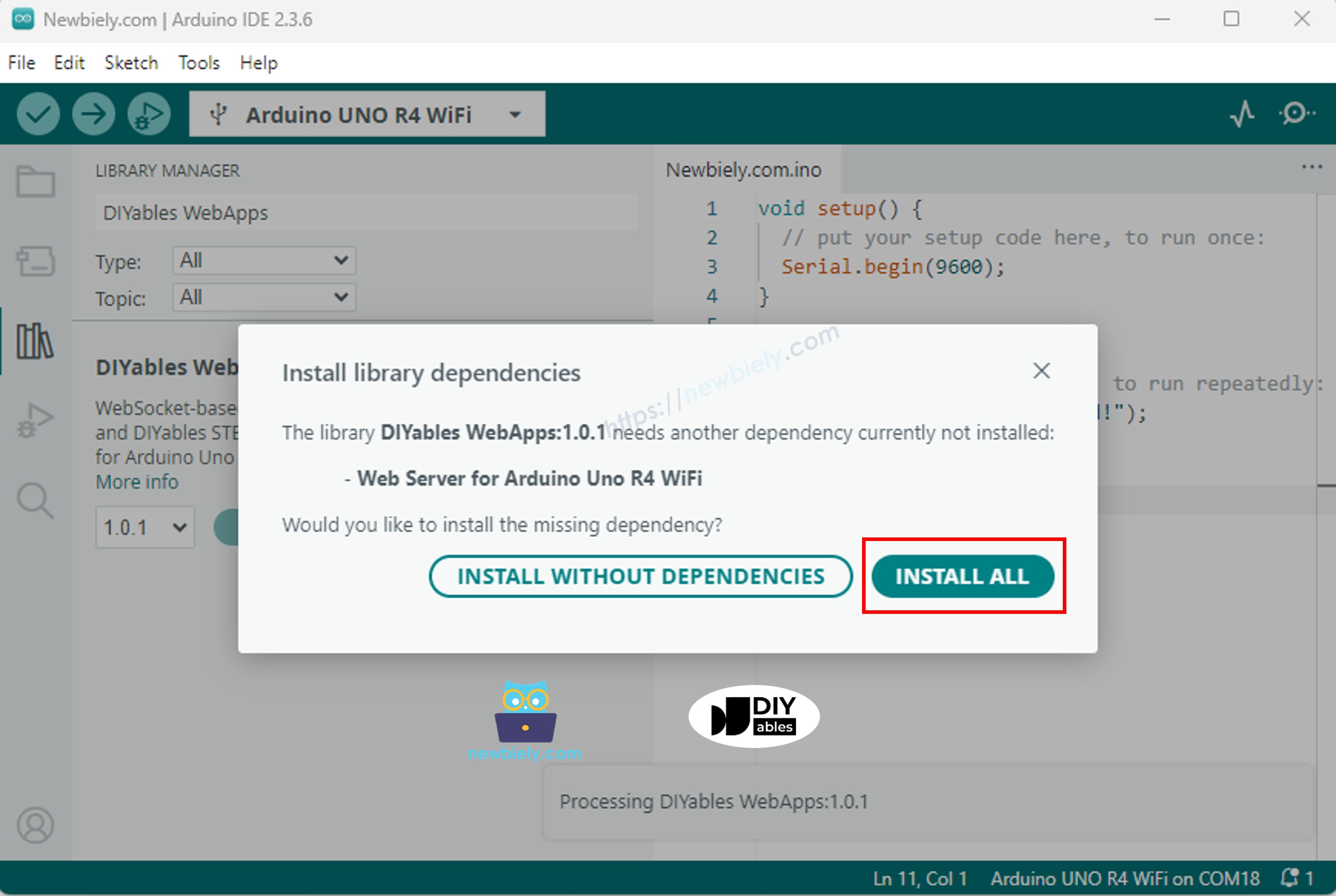
- Se le pedirá instalar algunas dependencias de otras bibliotecas
- Haga clic en el botón Instalar todo para instalar todas las dependencias de la biblioteca.
- En Arduino IDE, vaya a Archivo Ejemplos DIYables WebApps WebJoystick como ejemplo, o copie el código anterior y péguelo en el editor de Arduino IDE
- Configura las credenciales de WiFi en el código modificando estas líneas:
- Haz clic en el botón Subir en el IDE de Arduino para subir código al Arduino UNO R4/DIYables STEM V4 IoT
- Abre el Monitor Serial
- Revisa el resultado en el Monitor Serial. Se muestra a continuación.
- Si no ves nada, reinicia la placa Arduino.
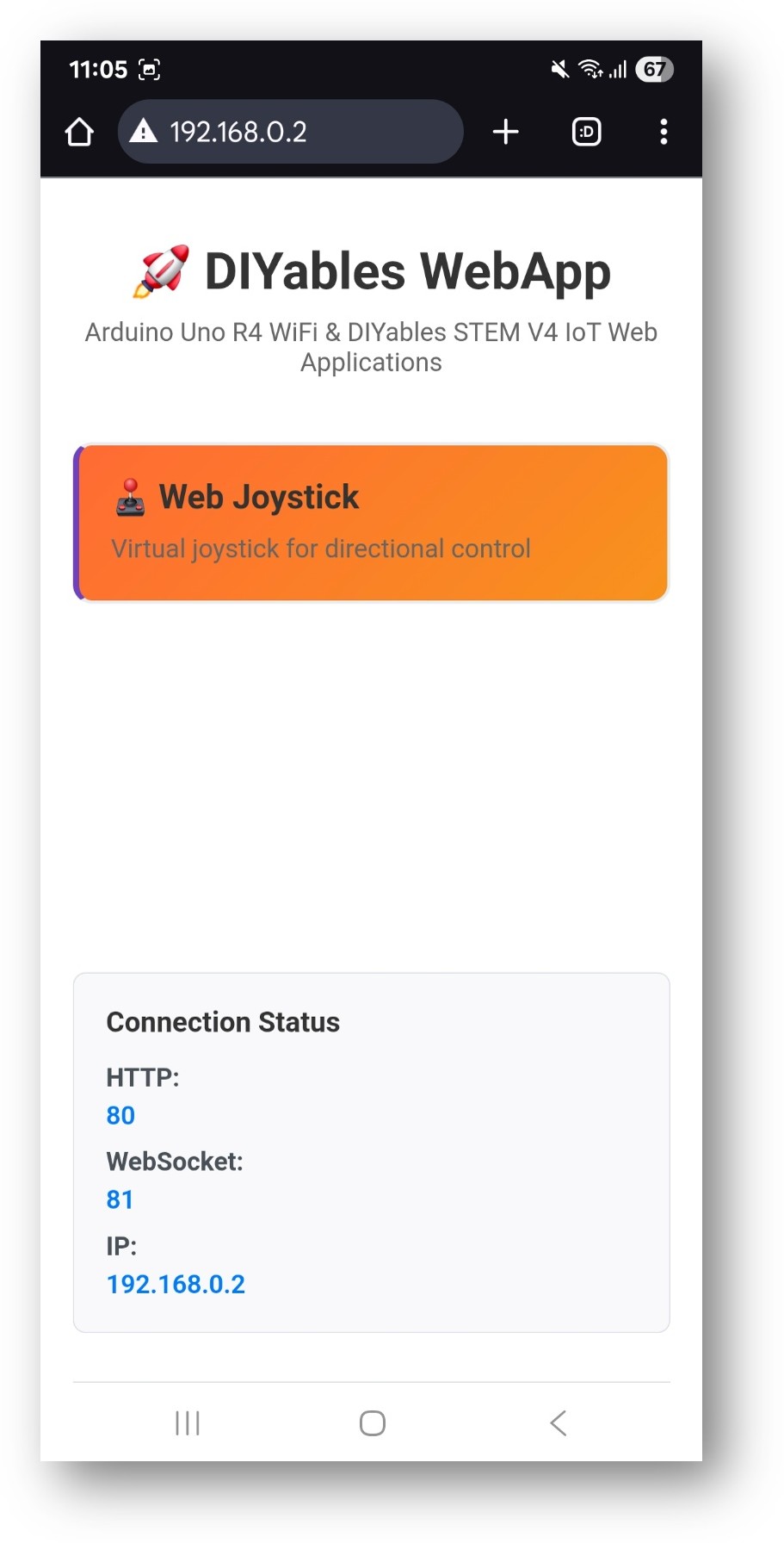
- Toma nota de la dirección IP que se muestra y escribe esa dirección en la barra de direcciones de un navegador web en tu teléfono inteligente o PC.
- Ejemplo: http://192.168.0.2
- Verás la página de inicio como en la imagen a continuación:
- Haz clic en el enlace de Web Joystick; verás la interfaz de usuario de la aplicación Web Joystick como la que se muestra a continuación:
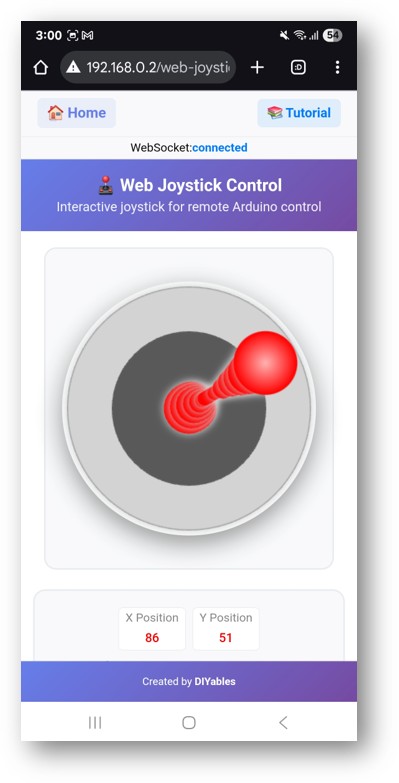
- O también puedes acceder a la página directamente mediante la dirección IP seguida de /web-joystick. Por ejemplo: http://192.168.0.2/web-joystick
- Intenta controlar el joystick virtual haciendo clic y arrastrando en el área del joystick y observa los valores de coordenadas X/Y (-100 a +100) en el Monitor Serial.
Personalización Creativa - Adapta el código a tu proyecto
2. Configurar los ajustes del joystick
El joystick se puede configurar con diferentes parámetros:
Configuración básica
Configuración avanzada
Cómo usar el joystick
Controles de la interfaz web
La interfaz del joystick proporciona:
- Área de mando del Joystick: Área de control circular para entrada táctil y por ratón
- Indicador de Posición: Muestra la posición actual del joystick
- Pantalla de Coordenadas: Valores X/Y en tiempo real (-100 a +100)
- Punto Central: Referencia visual para la posición neutral
Funcionamiento del joystick
Escritorio (Control del ratón)
- Haz clic y arrastra: Haz clic en el joystick y arrastra para moverlo
- Soltar: El joystick vuelve al centro (si autoReturn=true)
- Posición de clic: Haz clic directamente para establecer la posición del joystick
Móvil/Tableta (Control táctil)
- Toca y desliza: Toca el joystick y desliza el dedo para moverte
- Multitoque: Un dedo para control preciso
- Soltar: Regreso automático al centro (si está habilitado)
Sistema de Coordenadas
El joystick proporciona coordenadas en un sistema cartesiano estándar:
- Eje X: -100 (extremo izquierdo) a +100 (extremo derecho)
- Eje Y: -100 (extremo inferior) a +100 (extremo superior)
- Centro: X=0, Y=0 (posición neutral)
- Esquinas: Las posiciones diagonales proporcionan valores combinados de X/Y
Ejemplos de Programación
Manejador básico de joystick
Ejemplo de control de motor
Ejemplo de control de servomotor
Indicador de posición de LED
Configuración avanzada
Cambios de configuración en tiempo de ejecución
Implementación de la Zona Muerta
Rampa de velocidad
Ejemplos de Integración de Hardware
Control de Coche Robótico
Control del gimbal de la cámara
Control de color de LED RGB
Solución de problemas
Problemas Comunes
- Joystick no responde
- Verificar el estado de la conexión WebSocket en la consola del navegador
- Verificar la conectividad de red
- Actualizar la página del navegador
- Verificar el Monitor Serial en busca de errores
2. Movimiento entrecortado o irregular
- Aumentar el valor de sensibilidad para reducir la frecuencia de actualización
- Implementar filtrado de zona muerta
- Añadir rampas de velocidad para transiciones suaves
- Comprobar problemas de latencia de la red
3. El retorno automático no funciona
- Verifique la configuración de autoReturn: webJoystickPage.setAutoReturn(true)
- Verifique la compatibilidad del navegador (algunos dispositivos táctiles varían)
- Pruebe con diferentes métodos de entrada (ratón vs táctil)
- Valores que no alcanzan el rango completo
- Verificar la calibración del joystick en la interfaz web
- Verificar los cálculos de coordenadas en la función de devolución de llamada
- Probar con diferentes combinaciones de navegadores y dispositivos
Consejos de depuración
Añadir depuración exhaustiva:
Ideas de proyectos
Proyectos de Robótica
- Coche robótico con control remoto
- Control del brazo robótico
- Control de vuelo de dron (movimientos básicos)
- Navegación de robot para mascotas
Automatización del hogar
- Control de cortinas inteligentes (abrir/cerrar/posición)
- Control de paneo e inclinación de la cámara
- Control de brillo y color de la luz
- Control de velocidad y dirección del ventilador
Proyectos Educativos
- Herramienta de enseñanza de sistemas de coordenadas
- Demostraciones de control de motor
- Experimentos de posicionamiento de servomotores
- Interfaces de mandos para videojuegos
Arte y Proyectos Creativos
- Control de patrones de la matriz LED
- Control de visualización musical
- Control de robot de dibujo
- Instalaciones de arte interactivas
Integración con otros ejemplos
Combinar con WebSlider
Usa el joystick para la dirección y los deslizadores para la velocidad/intensidad:
Combinar con WebDigitalPins
Utiliza las posiciones del joystick para activar los estados de los pines digitales:
Próximos pasos
Después de dominar el ejemplo WebJoystick, intenta:
- WebSlider - Para control analógico adicional
- WebDigitalPins - Para control discreto de encendido/apagado
- WebMonitor - Para depurar valores del joystick
- MultipleWebApps - Combinando el joystick con otros controles
Soporte
Para ayuda adicional:
- Consulta la documentación de la API
- Consulta los tutoriales de DIYables: https://newbiely.com/tutorials/arduino-uno-r4/arduino-uno-r4-diyables-webapps
- Foros de la comunidad de Arduino
